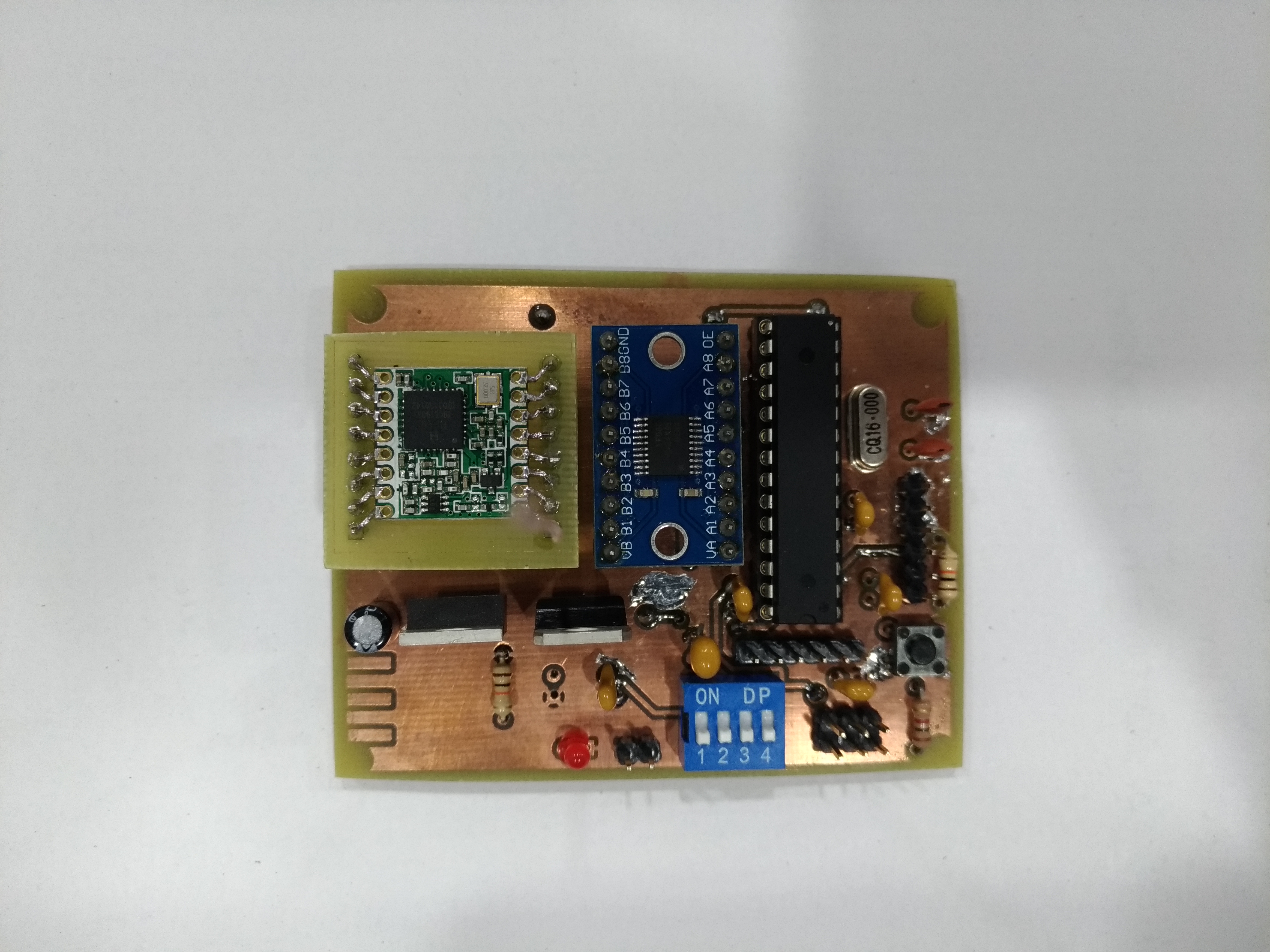
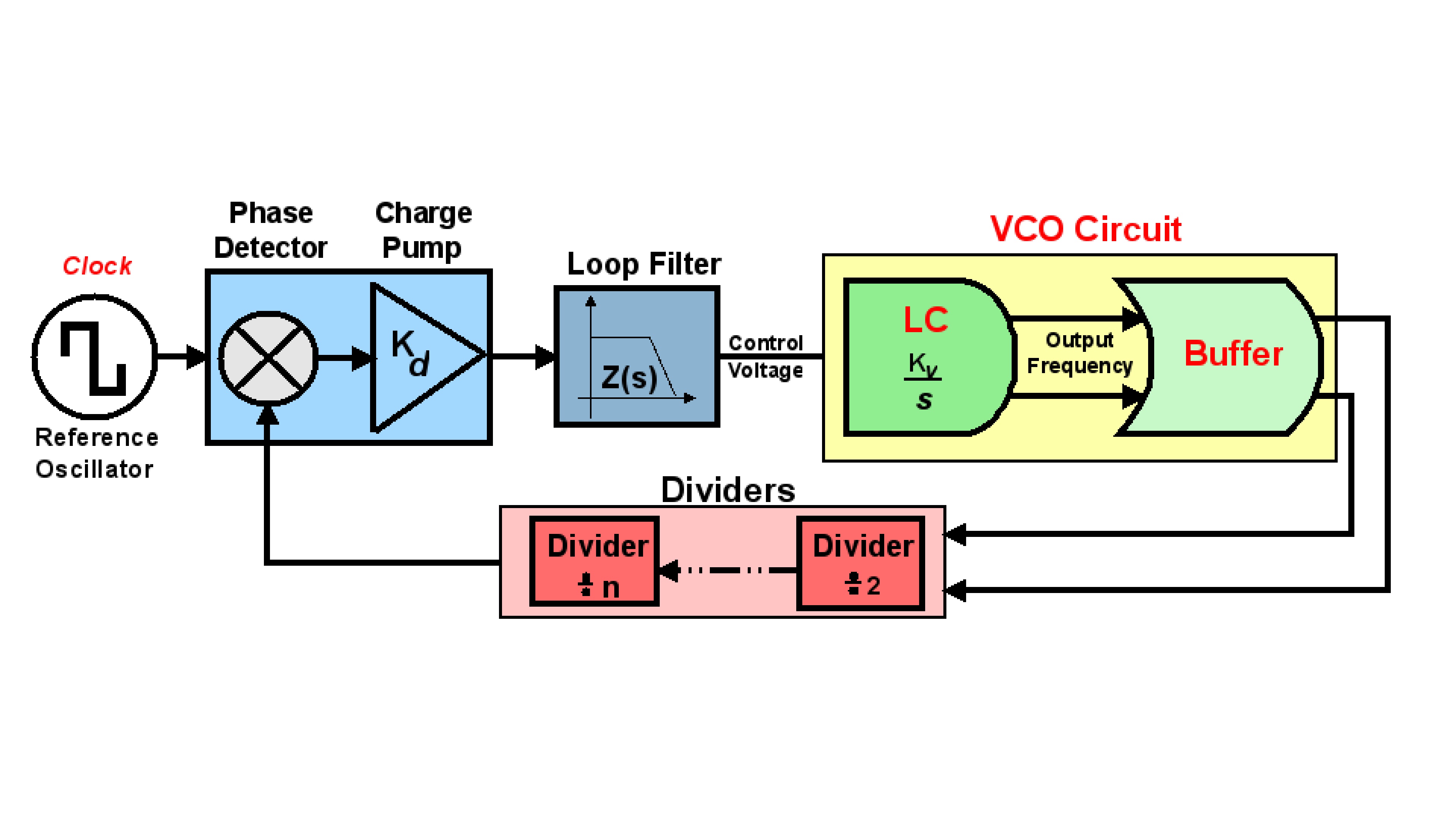
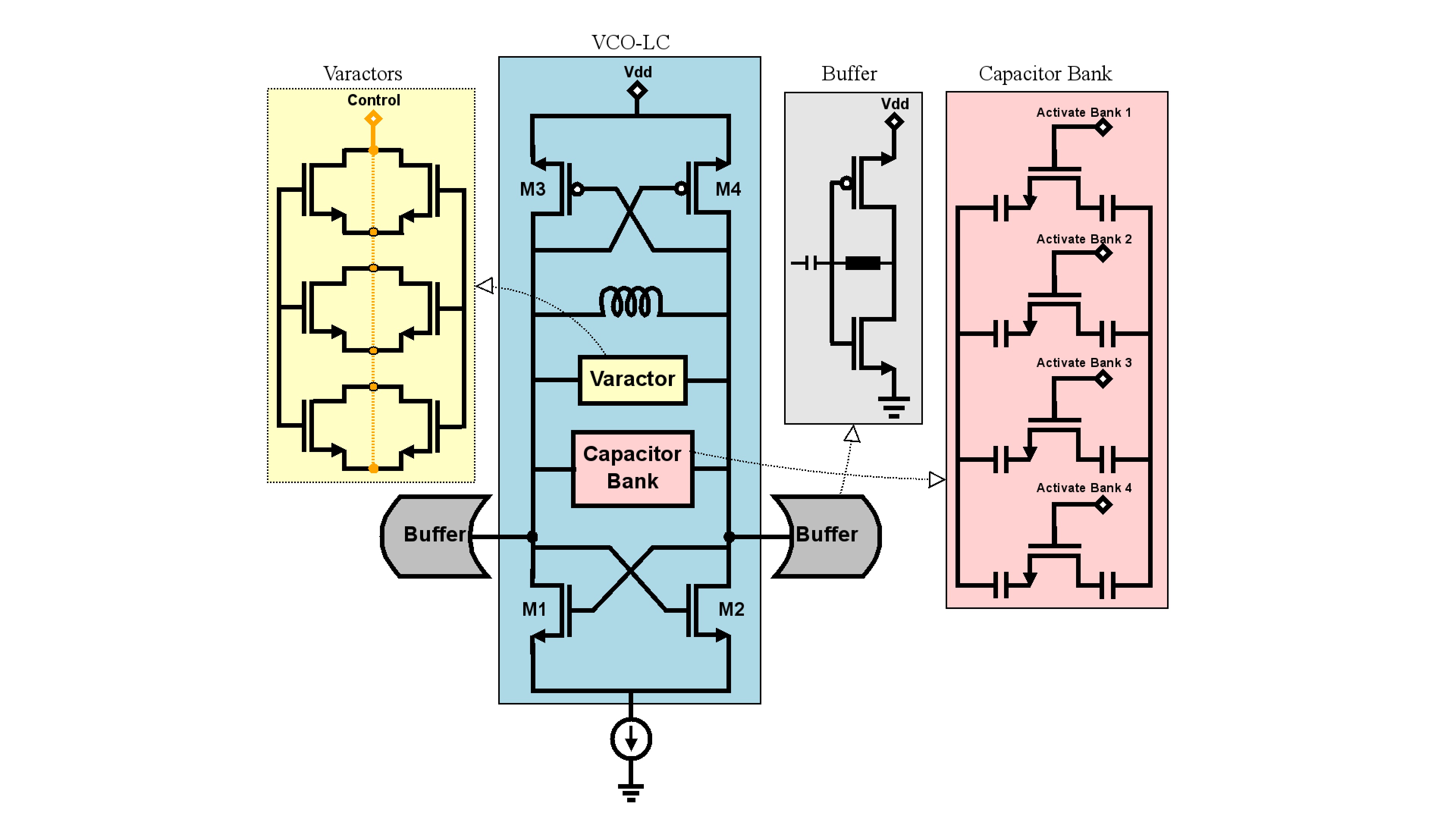
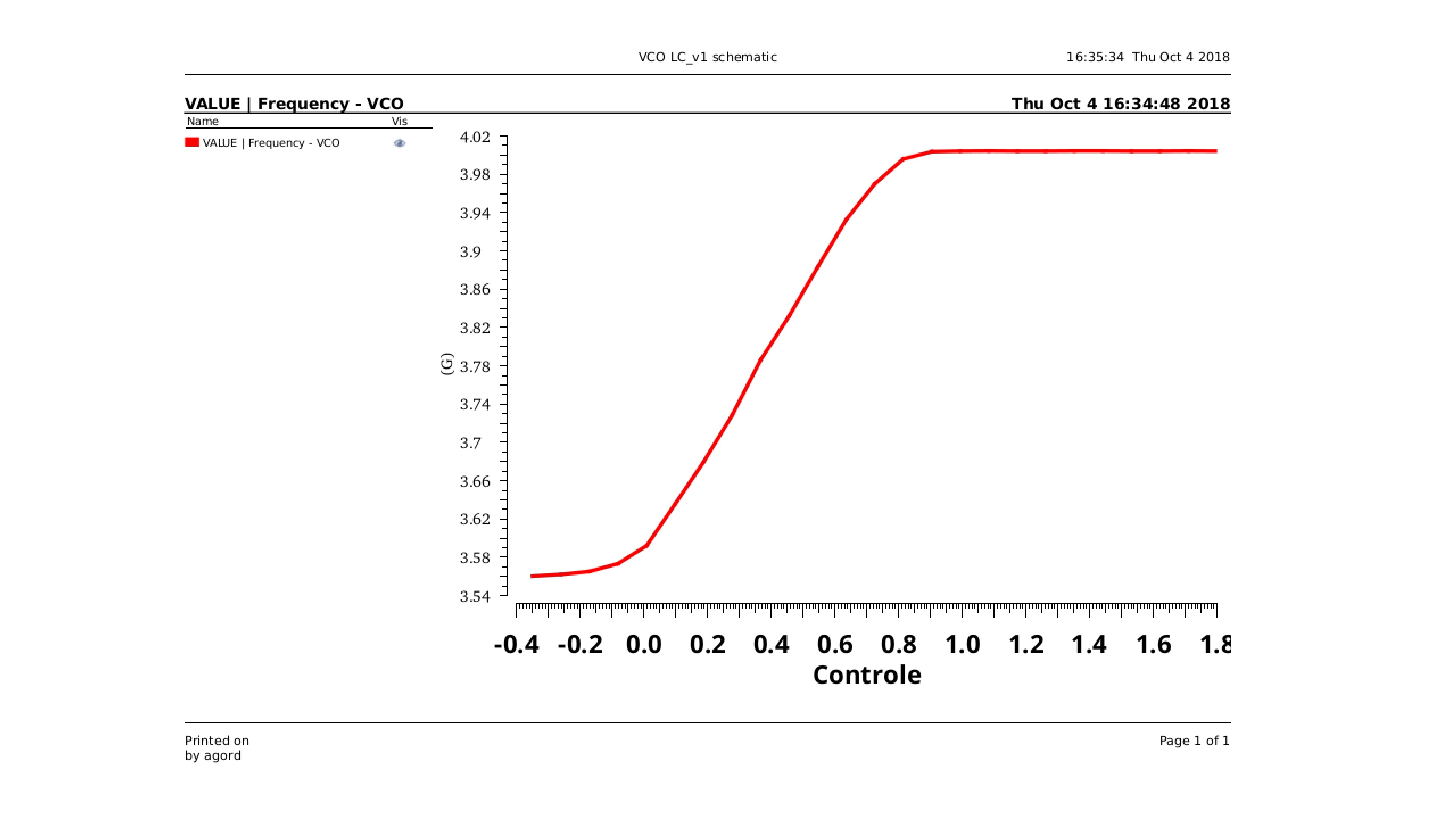
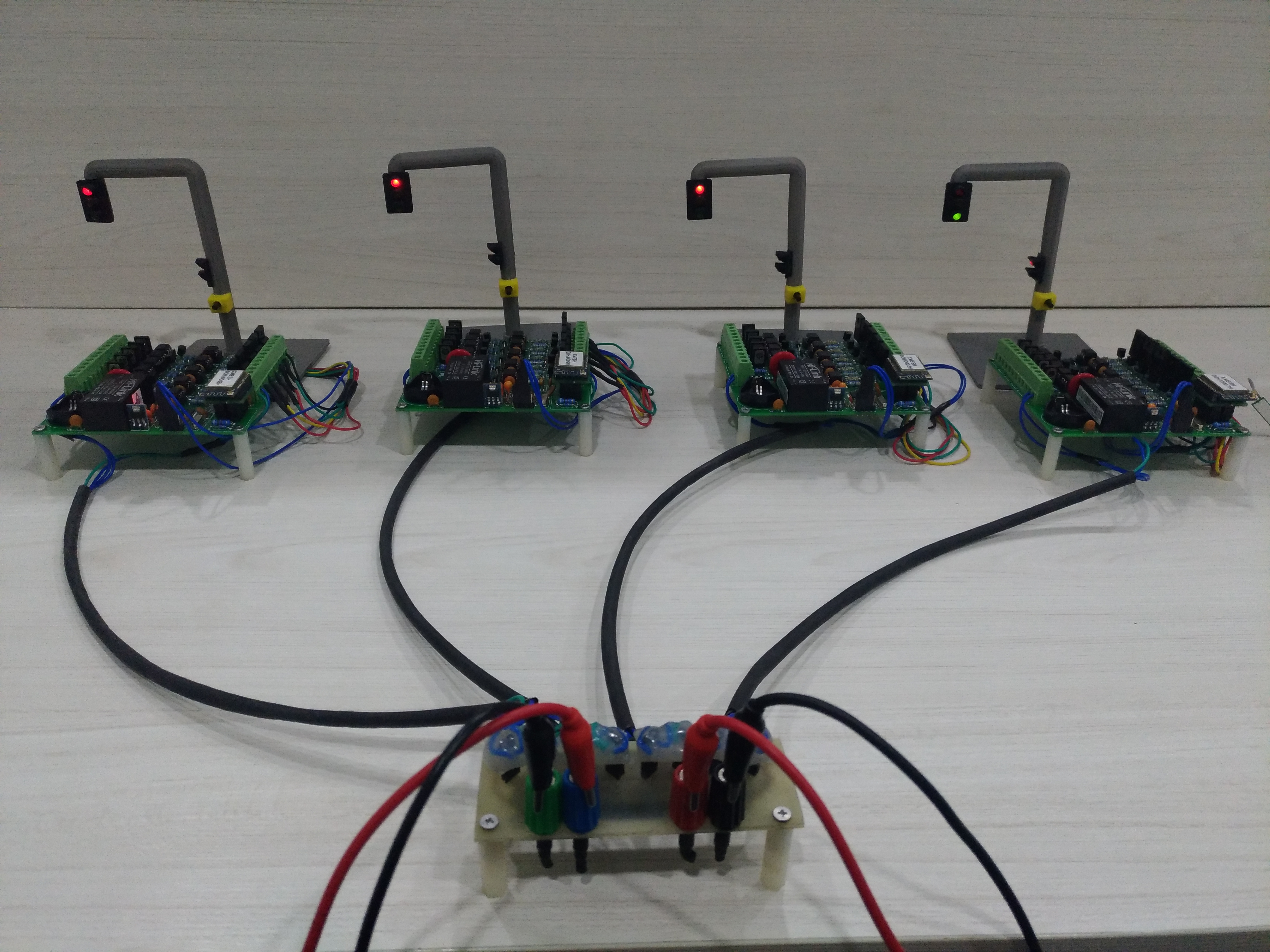
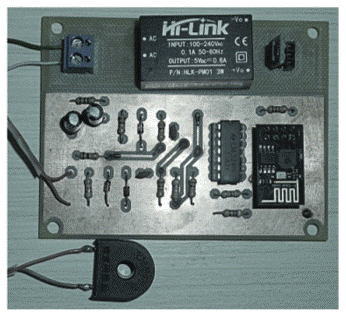
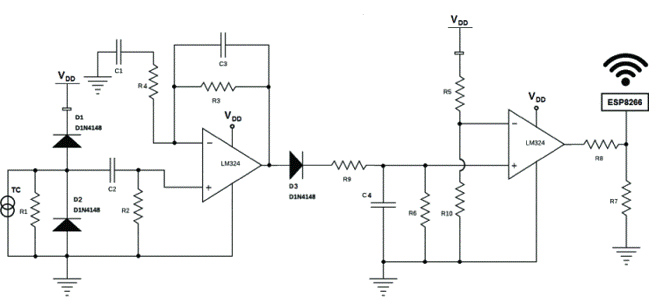
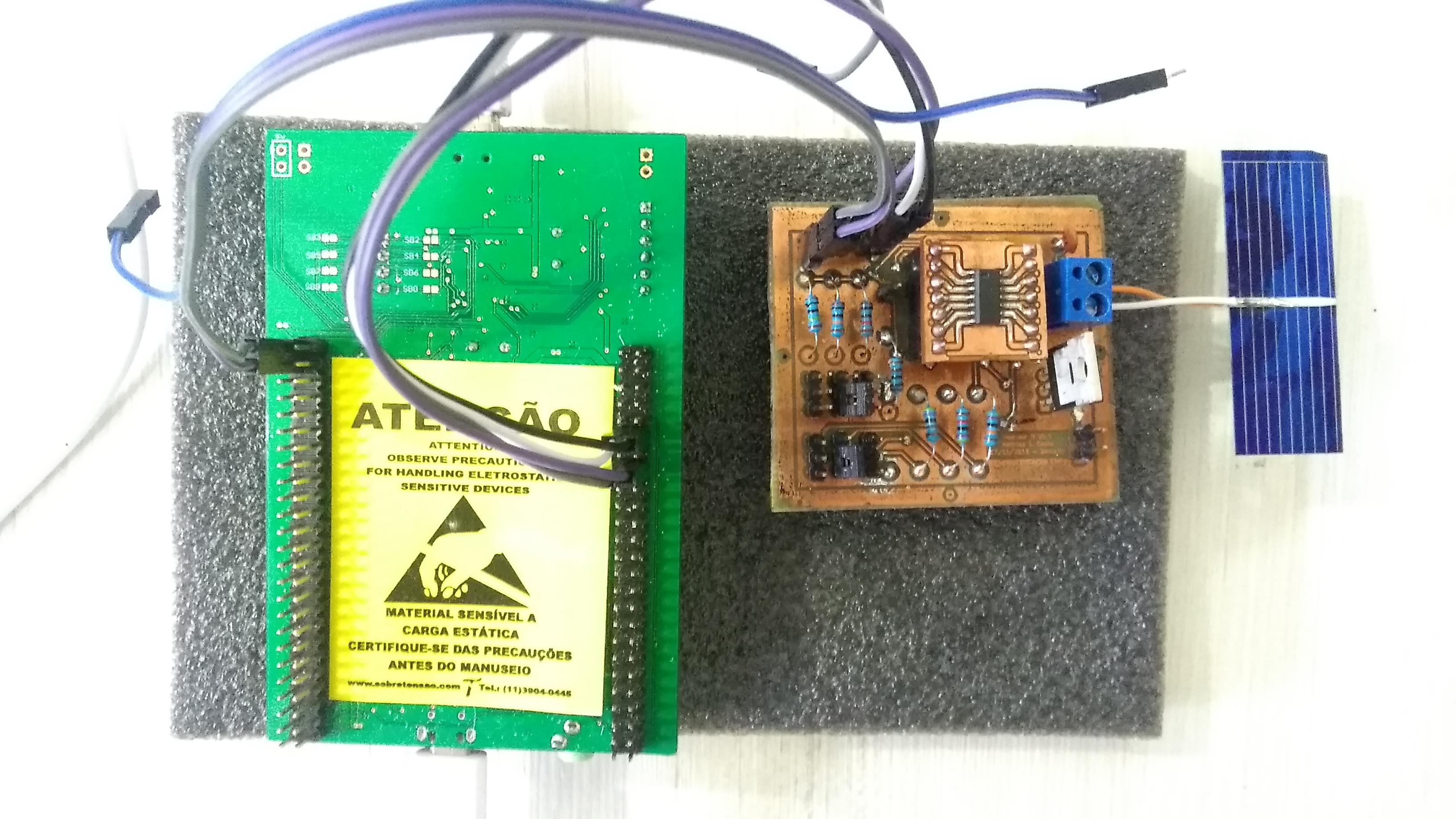
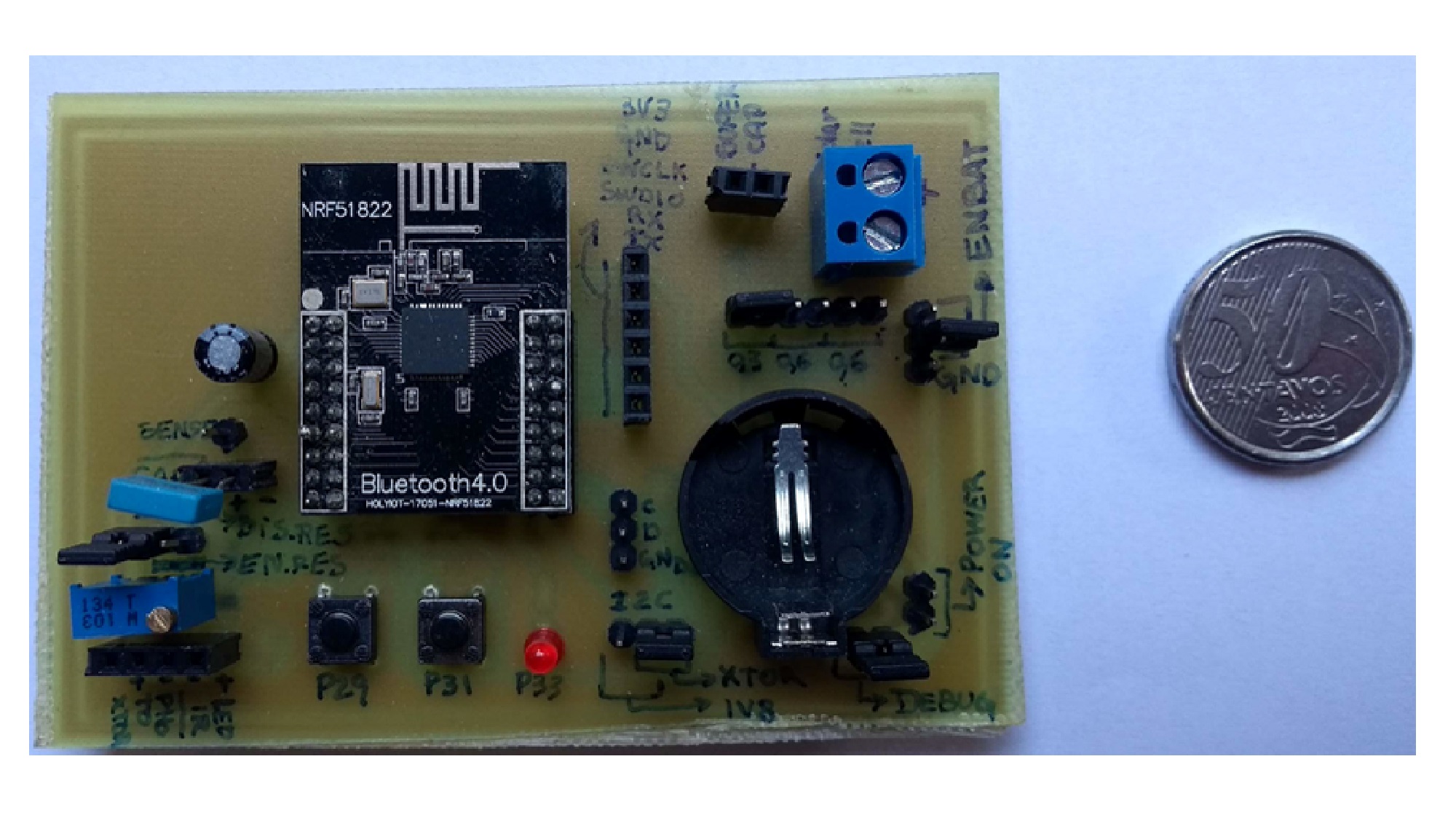
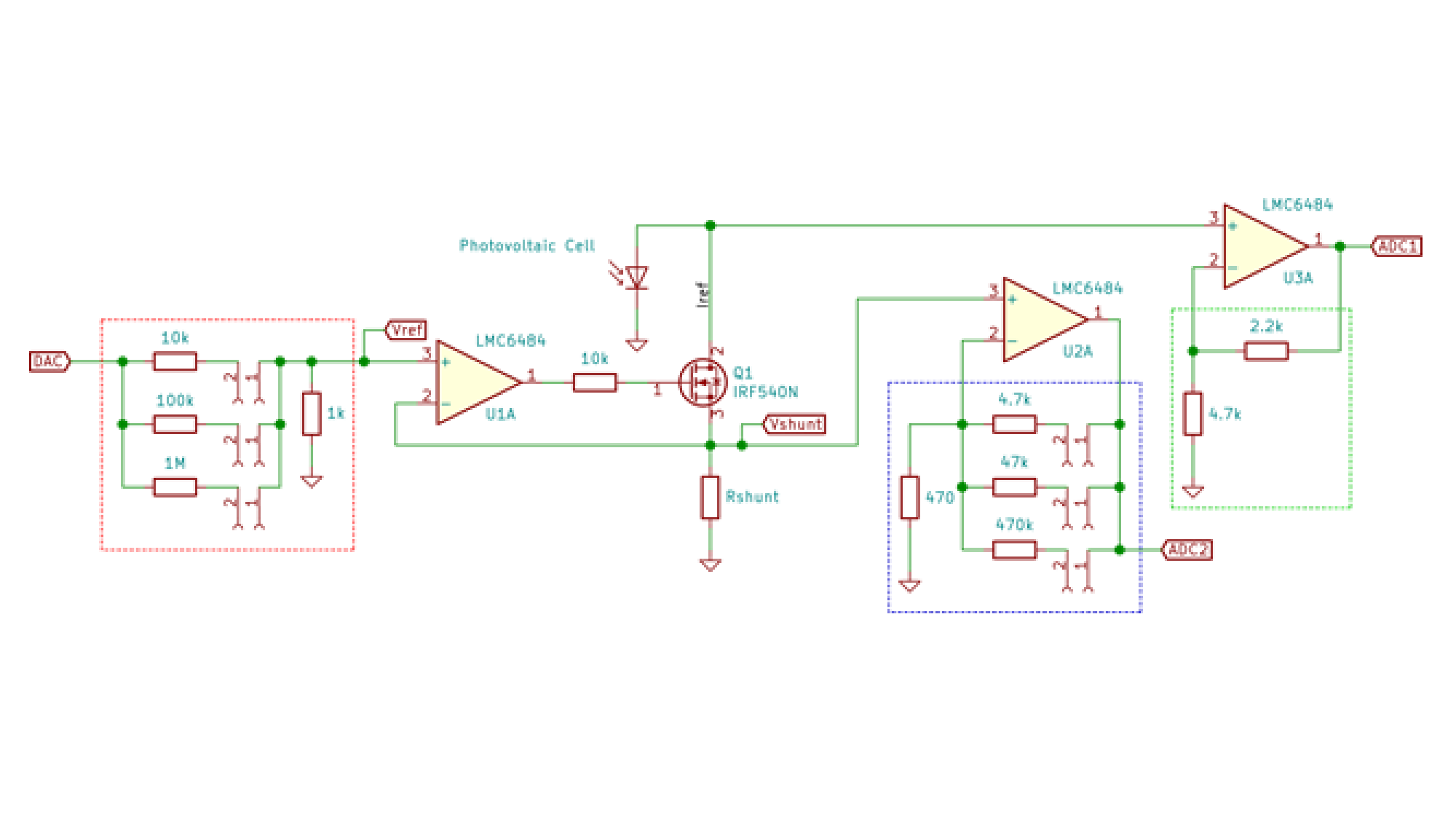
From its emergence to the present day, traffic lights control the traffic of vehicles. However, with the increase in the number of public (bus) and private vehicles (car, motorcycle and truck), urban centers are becoming more and more populous. Such phenomenon increases environmental and noise pollution and cause congestion issues. To stem the rise of such problems, large cities are adopting the use of technological devices, approaching the concept of smart cities. Examining only the traffic management systems, several hardware and software solutions are being studied and implemented around the world. This paper aims to contribute to traffic signal systems improvement, developing a centralized traffic light controller system through the use of a wireless communication network. In order to prove the system efficacy, of most commom types of urban intersections was carried out. Direct control routines were implemented for network traffic lights, providing the whole system control for extraordinary events, such as closing roads due to accidents or public events. Finally, it has drawn up safety routines, to report to the central management the operating status of the traffic lights system lamps. With the aid of a logic analyzer connected to the outputs for each focal group,it was possible to set up a operating stages temporal diagram of each traffic light. Thus, the system validation was made based on between theoretical and practical temporal diagrams similarity.
View Master's Thesis